Exploring the Beauty and Ecological Roles of Birds


Intro
Birds exist in every aspect of human life. Their chirping and colorful presence fascinate many individuals. Yet their significance extends beyond beauty and delight. This section examines how birds serve as critical factors in their ecosystems while also holding socio-cultural importance for humans. In this exploration, we consider a wide range of bird species that captivate our attention with their vibrant plumage and unique characteristics.
Understanding Your Pet
Birds that we keep as pets can bring joy and companionship. Understanding their behavior is essential for nurturing their well-being.
Pet Behavior Basics
Observing birds can reveal much about their emotional states. Many birds communicate through vocalizations and body language. A bird that fluffs its feathers may feel relaxed or comfortable. Conversely, a bird that hides or feathers down can express fear or stress. Providing a safe environment enhances their comfort and reduces anxiety.
Common Breed Characteristics
Different bird breeds exhibit unique traits. For example, parakeets, known for their playful nature, thrive in active environments. Finches are more sociable, often enjoying the company of their kind. Understanding these breed characteristics helps in planning suitable care and environments.
Species-Specific Needs
Each species has specific needs. Cockatiels, for example, enjoy social interaction and benefit from daily handling. On the other hand, canaries prefer solitude and may not thrive with excessive attention. Catering to these species-specific requirements promotes health and longevity.
Pet Care and Maintenance
Caring for birds effectively involves several key areas.
Feeding Guidelines
A balanced diet is vital. Seeds, pellets, and fresh vegetables should form the basis of their nutrition. Some birds, such as parrots, also require fruits in moderation. Providing clean, fresh water daily is equally important to their health.
Grooming Essentials
Grooming should not be overlooked. Regular feather baths are essential for maintaining feather quality. Clipping nails prevents discomfort, while beak care ensures proper feeding. Owners should familiarize themselves with these procedures or consult a vet for professional grooming advice.
Hygiene Practices
Keeping their cages clean is vital for bird health. Regular cleaning reduces the risk of illness. Remove uneaten food daily, and change bedding frequently to prevent bacteria build-up.
Training and Development
Training plays an important role in the well-being of birds.
Basic Commands and Skills
Teaching simple commands can enrich their lives. Start with basic commands like ‘step up’ or ‘down.’ These commands will improve communication and strengthen the bond between the bird and owner.
Behavioral Training Techniques
Using positive reinforcement techniques is essential. Reward good behavior with treats or praise. This encourages repetition of desired actions, resulting in a more well-behaved pet.
Addressing Common Behavior Issues
Understanding and addressing behavioral problems is crucial. Issues like biting or excessive screeching can arise from boredom or lack of interaction. Enriching their environments can solve many of these problems.
Health and Wellness
Maintaining health is essential for pet birds.
Routine Vet Check-ups
Regular veterinary check-ups help in early disease detection. Birds often hide illness symptoms, making vet visits fundamental. Annual check-ups should be routine to monitor health effectively.


Vaccination Needs
Some bird species may require vaccinations. Discuss with a vet recommendations based on the species owned. Vaccination establishes a baseline of protection against prevalent diseases.
Recognizing Signs of Illness
Awareness of illness signs improves outcomes. Symptoms like lethargy, loss of appetite, or abnormal droppings signal potential health problems. Immediate action is necessary to secure your pet's wellbeing.
Enrichment and Activities
Engaging birds in activities enhances their quality of life.
Indoor vs.
Outdoor Activities
Indoor birds need space to exercise. Providing a safe area for flight or toys encourages movement. Outdoor time, when safe, allows birds to explore and engage with natural stimuli.
Interactive Toys and Games
Interactive toys stimulate cognitive functions. Puzzle feeders challenge their problem-solving skills while providing enrichment. Rotate toys regularly to maintain interest.
Socialization Opportunities
Socializing your bird with other pets or humans is beneficial. Introduced carefully, birds can appreciate both human and avian interactions. This contributes to their mental stimulation and overall happiness.
Prolusion to Avian Beauty
The beauty of birds is not merely a superficial trait; it is intertwined with various aspects of their existence and roles in nature. In this section, we will explore why birds captivate human attention and the significance of their aesthetic appeal in our environment. Understanding avian beauty goes beyond mere admiration of colors and shapes. It encompasses an appreciation for their intricate behaviors, diverse adaptations, and ecological importance.
The allure of birds has profound implications. It fosters a deeper awareness of the natural world, encouraging conservation efforts and a cherished bond between humans and wildlife. Recognizing and understanding the characteristics that make birds beautiful also enriches our experiences in nature, enhancing our curiosity and respect for species that play critical roles in ecosystems.
Defining Beauty in Nature
Beauty in nature is subjective. While some might view it through the lens of vivid colors or graceful movements, others might consider harmony and balance as essential elements. Birds exhibit this complexity through their plumage, songs, and behaviors. Species such as the peacock demonstrate ostentatious beauty, while the subtle elegance of a sparrow can be equally appealing.
Factors contributing to the perception of beauty in birds include:
- Coloration: The range of colors in bird plumage can be astonishing, from the bright reds of the cardinal to the deep blues of the indigo bunting.
- Patterns: Many birds showcase intricate patterns that vary across species and even individual birds.
- Movement: The way birds wing their way through the air or hop along the ground can create a sense of grace and liveliness.
This dynamic interplay of features offers an opportunity for individuals to explore and engage with nature.
Birds as Symbols of Aesthetic Appeal
Birds often emerge as powerful symbols in art, culture, and literature. Throughout history, they have represented freedom, beauty, and the untamed spirit of nature. Many artists have sought to capture their essence in various forms, from paintings to sculptures. The works of John James Audubon, known for his detailed studies of North American birds, showcase avian beauty and the importance of preserving these species.
In literature, birds frequently serve as metaphors for many human emotions and experiences. The song of a nightingale symbolizes love and longing, while the soaring eagle represents ambition and strength. Their diverse places in human thought underline their universal appeal.
As we delve into this exploration of avian beauty, it becomes clear that these creatures hold a significant place in both nature and human culture. By recognizing their aesthetic qualities, we can start to appreciate the deeper connections they share with the ecological balance of our world.
Physical Attributes of Birds
The physical characteristics of birds play a significant role in both their aesthetic appeal and ecological functions. Their varied design elements contribute to the ways they interact with their environments, and understanding these attributes enhances our appreciation for their beauty. Birds exhibit a remarkable range of forms, colors, and specialized structures that not only elicit admiration but also serve vital ecological purposes.
Coloration and Patterns
Birds are often celebrated for their vibrant colors and unique patterns. The hues found in feathers can serve multiple functions, including camouflage, attracting mates, and warning predators. For example, the iridescent plumage of the hummingbird can shift in color based on the angle of light, mesmerizing anyone who observes it. Bright colors, such as those of the male peacock, are utilized in courtship displays to impress potential mates.
Additionally, patterning on feathers can influence behaviors. Striped or spotted patterns may help an individual blend into its surroundings, making it a challenging target for predators. Birds such as the American Woodcock rely on such colors and patterns to remain concealed in their habitats.
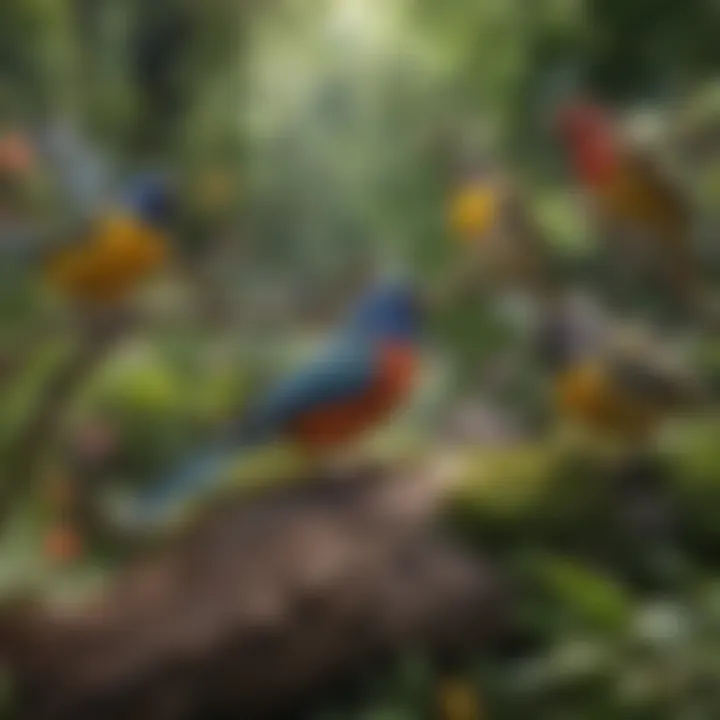

- Camouflage: Helps birds evade predators.
- Attraction: Bright colors attract mates.
- Communication: Color patterns can convey health status or readiness to mate.
Understanding these aspects of coloration and patterning is vital for birdwatchers and ecologists alike, as it helps interpret behavior and ecology.
Size and Structural Diversity
Size among bird species is a remarkable area of interest. Birds range from the tiny bee hummingbird, measuring just about 2.2 inches, to the towering ostrich, reaching up to 9 feet tall. This size diversity is not just a matter of aesthetics; it influences their ecological roles and adaptations. The size of a bird can determine its feeding habits, nesting styles, and predator-prey interactions.
Structural variations are equally significant. Birds have evolved a range of beak shapes and sizes tailored to their diets. For instance, the long, slender beak of the hummingbird is perfect for accessing nectar in flowers, while the stout beak of a hawk allows for tearing flesh. Similarly, variations in wing shape affect flight patterns and abilities, enabling some species to soar great distances while others are more suited for quick maneuvers in dense habitats.
- Dietary Adaptation: Beak shapes indicate diet.
- Flight Mechanics: Wing structures affect flight behavior.
This aspect of physical attributes not only provides insight into evolutionary adaptations but also informs conservation efforts by highlighting species' specific needs in their environments.
Unique Adaptations
Birds are often equipped with extraordinary adaptations that serve both aesthetic and functional purposes. Some species exhibit specialized features that directly affect their survival. The Arctic tern, for instance, has long wings designed for effortless gliding during long migrations. These adaptations not only enhance their ability to travel vast distances but also contribute to their unique appearance.
Other peculiar adaptations can be seen in the way some birds have evolved certain physical traits for specific functions. The bill of the flamingo is uniquely adapted to filter-feed in shallow water. Such adaptations reveal how morphology relates to ecological niches and survival strategies within ecosystems.
- Migration: Wing designs facilitate long flights.
- Feeding Specializations: Unique beak shapes support specific diets.
Birds' unique adaptations emphasize the intricate relationship between form and function, showcasing how beauty is interwoven with ecological significance.
Ecological Impact of Birds
Birds play essential roles in the ecosystems where they reside. Their ecological impact is multifaceted, spanning from facilitating plant reproduction to maintaining ecological balance. These functions are critical not only for the health of the ecosystems but also for human well-being. Their contributions in biodiversity support have lasting effects on both flora and fauna.
Pollination and Seed Dispersal
Birds contribute significantly to pollination and seed dispersal. Many plants depend on birds for effective pollination, which leads to the production of valuable fruits and seeds. For instance, the hummingbird is known for its role in pollinating various flowering plants, thriving on nectar. This interaction ensures genetic diversity and the survival of plant species.
Moreover, birds like frugivores (fruit-eating birds) consume ripe fruits and help in the dispersal of seeds. This behavior aids in the growth of new plants in different locations. By relocating seeds, birds contribute to a more diverse plant community, which is vital for the health of the habitat.
Key benefits of this ecological impact include:
- Enhanced plant diversity
- Improved ecosystem resilience
- Support for wildlife habitats
Pest Control and Ecosystem Balance
Birds are also key players in pest control. Many species, such as the American Robin and the House Sparrow, feed on insects. This predatory behavior helps regulate insect populations, ensuring that no single species overpopulation disrupts the ecological balance. By managing pests, birds protect crops and promote healthier gardens and farms.
Additionally, the presence of birds indicates a healthy ecosystem. They serve as indicator species, reflecting the state of their environment. If bird populations are thriving, it is often a signal that other wildlife is also doing well. Conversely, declines in bird populations may indicate ecological distress.
The overall advantages of birds in pest control and balance include:
- Reduction of harmful insect populations
- Indicators of environmental health
- Maintenance of biodiversity through predator-prey relationships
“Birds don’t just beautify our environment; they are integral in keeping it balanced and thriving.”
Understanding the ecological impact of birds reveals their necessity beyond aesthetics. Their roles in pollination, seed dispersal, and pest control underscore the interconnectedness of beauty and environmental health. Recognizing this allows for a greater appreciation of their place in our world's ecosystems.
Birds in Cultural Context
The significance of birds in cultural contexts cannot be overstated. Their presence across various societies often intertwines with themes of freedom, beauty, and spirituality. Birds touch many aspects of human life, influencing art, literature, mythology, and recreational activities like birdwatching. This relationship enriches our understanding of these creatures and highlights their roles beyond the natural world.
Birds in Art and Literature
From ancient times to modern literature, birds have served as potent symbols and subjects of artistic expression. In art, they are frequently depicted for their striking beauty and grace. For instance, the vibrancy of peacocks often captures the attention of painters and photographers alike. Works by artists such as John James Audubon illustrate not just the artistic beauty of birds but also their ecological significance.

In literature, birds appear as metaphors for various themes. In many classic texts, such as those by William Blake or Emily Dickinson, birds symbolize freedom, aspiration, or even the soul. These interpretations provide a richer comprehension of human emotion and experience, through the lens of avian representation. Therefore, exploring how birds are presented in art and literature can lead to a deeper appreciation of their roles in shaping cultural narratives.
Symbolism and Mythology
Birds have long been associated with a myriad of symbols across different cultures. In many traditions, they serve as messengers between the earthly and spiritual realms. For instance, in Native American mythology, the eagle often symbolizes strength and courage, while the hummingbird represents love and joy. Each culture assigns unique meanings to specific bird species, reflecting their societal values and beliefs.
Furthermore, birds are frequently woven into various mythological narratives. These tales often position birds as central figures, embodying lessons or moral teachings. For example, the story of the phoenix illustrates rebirth and renewal, while the owl is often perceived as a symbol of wisdom. Understanding these symbols allows for a broader appreciation for how birds are interwoven with human culture and thought.
Birdwatching as a Cultural Pursuit
Birdwatching has evolved into a beloved cultural pastime, attracting a diverse audience from families to seasoned naturalists. This activity fosters a deeper connection with nature. Observing birds in their habitats not only helps individuals develop appreciation for avian life but also encourages mindfulness and environmental awareness.
Many communities organize local birdwatching events or workshops to engage families and foster education about avian species. These gatherings often lead to positive interactions among participants, building a sense of community and shared responsibility for local ecosystems. Additionally, the rise of mobile applications for birdwatching has made it more accessible to people of all ages, thus promoting conservation efforts.
In summary, the cultural context of birds often reflects our values, beliefs, and connections to nature. Through art, literature, symbolism, and recreational activities like birdwatching, we can explore the multifaceted roles that birds play in human society, ultimately enhancing our understanding of their aesthetic and ecological significance.
The Role of Birds in Biodiversity
Birds play a crucial role in maintaining the health of ecosystems. Their various behaviors and interactions with other species contribute to biodiversity, an essential aspect of environmental stability. The presence of bird species can indicate the overall condition of an ecosystem, thus making them integral to the study of environmental health. Recognizing the benefits birds provide can enhance our appreciation for them beyond their aesthetic qualities and emphasize their ecological importance.
Indicator Species and Environmental Health
Birds are often referred to as indicator species because their presence and population dynamics can reveal vital information about the environment. For instance, certain bird species, such as the American robin or the yellow warbler, are sensitive to changes in habitat quality. When their numbers decline, it can signal problems such as habitat destruction, pollution, or climate change.
Monitoring bird populations offers insights into broader ecological trends. By studying their behaviors, such as migration patterns or breeding success, scientists can evaluate the health of various ecosystems. Healthy bird populations generally correlate with well-functioning ecosystems, while declines often indicate larger systemic issues. This relationship underlines the necessity of ongoing research and conservation efforts focused on birds.
"The presence of diverse bird species is more than a sign of beauty; it is a litmus test for environmental health."
Birds contribute positively to their ecosystems in other ways. For example, they can control insect populations, pollinate plants, and disperse seeds. Each of these functions helps maintain ecological balance. Importantly, thriving bird populations can enhance biodiversity, which reinforces the resilience of ecosystems against climate change and other environmental stressors.
Conservation Efforts and Challenges
Despite their crucial roles, birds face numerous threats globally. Habitat loss due to urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation poses significant challenges to bird populations. Pollution, both chemical and plastic, further endangers many species. Climate change also alters habitats and food availability, making survival increasingly difficult.
Conservation efforts are essential to mitigate these challenges. Organizations like the Audubon Society and the World Wildlife Fund work tirelessly to protect bird habitats and species. Rehabilitation programs, public awareness campaigns, and legislative advocacy are some methods they employ. Additionally, community involvement in local conservation initiatives can foster a sense of stewardship and responsibility.
However, conservation efforts face obstacles. Funding can be insufficient, and the prioritization of ecosystem conservation often competes with economic growth initiatives. Global cooperation and commitment are crucial for effective conservation strategies. Without decisive action, many bird species may face extinction, which would further destabilize their ecosystems.
To conclude, the role of birds in biodiversity is not only a testament to their ecological functions but also a reflection of our interdependence with nature. Recognizing their significance encourages responsible stewardship of our environment.
End: Appreciating Avian Diversity
The exploration of avian beauty and ecology reveals much about the interconnectedness of life on Earth. As we reflect on the unique aspects of birds—from their colors to their roles in ecosystems—it becomes clear why they captivate so many. Appreciating avian diversity is not just about admiring their looks; it involves understanding their vital role in maintaining ecological balance.
The Interconnectedness of Beauty and Ecology
Birds represent the harmony between aesthetic appeal and ecological significance. Their beauty often attracts human interest, fostering a desire to engage with nature. This engagement can lead to conservation efforts. For instance, the striking plumage of the Scarlet Macaw draws admiration but also highlights the need for habitat preservation. Recognizing this interconnection encourages a deeper respect for birds, motivating us to protect their environments.
Birds contribute to numerous ecological processes, such as:
- Pollination of plants
- Seed dispersal
- Pest control
Each of these roles is critical for sustaining ecosystems. When we admire a bird’s beauty, we are also appreciating its contributions to the health of our planet.
“Beauty varies widely across species, yet every bird holds a unique ecological position.”
Future Perspectives on Bird Conservation
As humanity faces environmental challenges, the future of bird conservation grows increasingly important. Conservation initiatives must evolve to address habitat loss, climate change, and pollution impact. This requires collaboration among scientists, activists, and communities.
Effective strategies might include:
- Establishing protected areas for diverse bird species
- Restoring degraded habitats
- Conducting research on avian migration patterns
Raising awareness through education can foster a sense of responsibility toward avian life. Families and pet owners can play a role by supporting conservation organizations and participating in local birdwatching events. These actions can create a culture that values and protects avian diversity.
In summary, the appreciation of birds extends beyond their beauty. Embracing both their aesthetic qualities and ecological roles enhances our understanding of the natural world. By prioritizing conservation efforts, we can ensure that future generations will also enjoy the beauty and benefits birds provide.







