Understanding Finch Nestlings: Development and Care


Intro
Finch nestlings represent a crucial phase in the lifecycle of these small avian species. Understanding their development, care, and conservation is essential not only for pet owners but also for bird enthusiasts and conservationists. This section provides an in-depth look into the various dimensions of finch nestlings, addressing essential aspects of their biology, caregiving practices, and environmental challenges. As the habitat for many finch species diminishes due to urban expansion and climate change, it becomes imperative to gain knowledge about their behaviors, needs, and the measures necessary to protect them.
Understanding Your Pet
When considering finch nestlings as pets, one must first grasp their specific behavioral traits and the requirements they have in a domestic setting. Knowing these aspects can make a distinct difference in their development and overall well-being.
Pet Behavior Basics
Finch nestlings, like other animals, exhibit a range of behaviors that inform their needs and interactions. They are naturally social creatures, often thriving in groups. This socialization is critical during their early growth stages, promoting healthy behaviors as they mature. Moreover, their interactions with guardians can shape their adaptability to familiar environments.
Common Breed Characteristics
Different finch breeds, such as the Gouldian finch or Zebra finch, possess unique characteristics. For instance, the Gouldian finch is known for its vibrant colors and distinctive calls. Understanding these traits helps in appreciating their behavior and addressing their specific care requirements. Recognizing breed characteristics can guide owners in ensuring they provide an appropriate habitat and environment for these birds.
Species-Specific Needs
Finch nestlings have distinct needs based on their species. For example, some finches require a more balanced diet than others or prefer specific nesting materials. It is pivotal for owners to research their specific breed to provide optimal care. A nuanced understanding of these needs can enhance the quality of life for the nestlings.
Pet Care and Maintenance
The care of finch nestlings extends beyond simply providing basic sustenance. Owners must adopt a holistic approach that includes feeding, grooming, and hygiene practices.
Feeding Guidelines
Offering a diet that mirrors their natural food sources is essential. Finch nestlings typically consume a mix of seeds, fruits, and insects in the wild. A commercial feed like Kaytee Forti-Diet Pro Health is a well-balanced option. Supplementing their diet with soft foods, such as mashed fruits or specially designed nests for finch nestlings, promotes healthy growth and development.
Grooming Essentials
Grooming is fundamental to maintaining a finch's health. Regular feather checks are necessary to prevent conditions like feather cysts. Their nails may also require occasional trimming to prevent injury to themselves or other birds.
Hygiene Practices
Cleanliness is critical in providing care for finch nestlings. Their cages should be regularly cleaned, avoiding the buildup of waste or uneaten food. This not only preserves a healthy living environment but also protects them from potential diseases.
Training and Development
Training finch nestlings is more about interaction and socialization than strict commands. It is essential to understand that these birds learn through observation and mimicry.
Basic Commands and Skills
While training finch nestlings in the traditional sense may not be applicable, encouraging behaviors like coming to a particular area could be beneficial. Use positive reinforcement, rewarding behavior with treats, to promote this action.
Behavioral Training Techniques
The application of simple techniques, such as consistent interaction and exposure to different stimuli, helps in shaping behavior. Providing a range of materials can stimulate finch nestlings' exploration and learning.
Addressing Common Behavior Issues
Common issues may arise, such as excessive chirping or aggression. Identifying the root cause—whether due to stress or lack of space—can aid in addressing these problems. Ensuring they have varied environmental enrichment reduces behavioral issues significantly.
Health and Wellness
Maintaining the health of finch nestlings is paramount. This can be achieved through regular vet check-ups, vaccinations, and being observant for signs of illness.
Routine Vet Check-ups
Routine check-ups should be a part of the care regimen for finch nestlings to catch any health issues early. Avian veterinarians can provide essential vaccinations and health advice tailored to specific finch species.
Vaccination Needs
Vaccinations are vital to preventing common avian diseases. It is necessary to consult with veterinarians regarding which vaccines are suitable for finch nestlings.
Recognizing Signs of Illness
Awareness of illness indicators is essential for early intervention. Symptoms such as lethargy, changes in appetite, or abnormal droppings are critical signals that should prompt a consultation with a vet.
Enrichment and Activities
Providing enrichment and activities is crucial for the mental and physical well-being of finch nestlings. It's important to strike a balance between indoor and outdoor activities.
Indoor vs. Outdoor Activities
Indoor activities can include various perches, swings, and toys that promote exercise and engagement. Outdoor time, if safe and controlled, can expose them to natural elements, enhancing their sensory experiences.
Interactive Toys and Games
Toys should be varied; for example, simple swings or toys that mimic foraging activities can promote physical activity, ensuring they engage their instincts and curiosity.
Socialization Opportunities
Finch nestlings benefit significantly from socialization with other finches. Providing opportunities for interaction encourages bonding and learning within their species context.
Understanding and caring for finch nestlings is not just about their needs; it is a responsibility that enhances their lives and contributes to conservation efforts.

In doing so, we contribute collectively to the survival and flourishing of these remarkable birds.
Foreword to Finch Nestlings
Understanding finch nestlings is pivotal for anyone interested in avian biology, conservation, and responsible pet ownership. Nestlings are in a critical stage of development, and comprehending their needs is crucial for their survival. This section will delve into what makes finch nestlings exceptional and why their care is significant for their growth and future.
Defining Nestlings
Nestlings are the juvenile birds that have recently hatched. They are entirely dependent on their parents for food, warmth, and protection. Anatomically, finch nestlings are characterized by their undersized bodies, closed eyes, and often, lack of feathers during the initial days of life. Typically, they remain in the nest for several weeks, gradually growing and developing crucial skills necessary for survival.
The period of being a nestling significantly influences a finch's future capabilities. During this time, nestlings acquire essential traits from their environment and parental influences. In the wild, most finch species will exit the nest after about two to three weeks, a period filled with intense vulnerability yet vital learning experiences.
The Importance of Finch Nestlings
Addressing the significance of finch nestlings goes beyond mere biological interest. They play a crucial role in the ecosystem as they contribute to the biodiversity of their habitats. Healthy populations of finches can help maintain ecological balance, providing various services, such as seed dispersal and insect population control.
Additionally, understanding their development process holds great import for enthusiasts and conservationists alike. Awareness of the challenges faced by nestlings can lead to better protective measures through humane interventions. This understanding can also elevate the care practices among pet owners, ensuring that those who choose to care for finches are well-equipped to foster their well-being.
"Nestlings are not just the future of their species; they represent the interconnectedness of our ecological systems."
Ultimately, a thorough understanding of finch nestlings empowers individuals to advocate effectively for their conservation. By fostering knowledge, we can contribute positively to the survival and prosperity of these captivating avian creatures.
Life Cycle of Finch Nestlings
The life cycle of finch nestlings is a critical aspect that highlights the development and growth stages of these birds. It provides insight into how these young finches transition from egg to fledgling. Understanding the life cycle is essential for various reasons. It helps in identifying the specific needs and care required during each stage, aiding pet owners and enthusiasts in better nurturing and supporting these birds. Moreover, recognizing the vulnerabilities that each life stage presents can enhance conservation efforts. The life cycle can be broken down into several key elements: egg development and hatching, early growth stages, and the fledging process.
Egg Development and Hatching
Finch eggs have a delicate structure, typically speckled or patterned, which assists in camouflage. The incubation lasts about 12 to 14 days, depending on species and environmental conditions. During this time, the female finch plays a significant role. She ensures that eggs remain warm and is responsible for turning them regularly, which is essential for proper development.
Factors that Affect Egg Development:
- Temperature and Humidity: Consistent and proper conditions are crucial.
- Nest Location: Predator threats can impact the hatching success.
Once fully developed, the eggs will hatch. Hatchlings are altricial, meaning they are born quite helpless, with closed eyes and few feathers. This stage is marked by the chicks' intense reliance on parental care for survival.
Early Growth Stages
Following hatching, the nestlings enter the early growth stage, where they undergo significant physical and physiological changes. In this period, they develop feathers quickly, crucial for mobility and protection. The nestlings rely entirely on the parents for food, often being fed a diet rich in protein and administered as regurgitated food by the adults.
During the first few days, the nestlings begin to develop their vision and hearing capabilities. These sensory developments are vital for communication and interaction with their parents and siblings. The parental role during this stage is foundational.
Key Development Aspects:
- Weight Gain: Healthy weight is crucial for overall growth.
- Social Interactions: Early interactions with siblings can promote social skills.
Fledging Process
The final phase of the life cycle is the fledging process. This is when nestlings prepare to leave the nest and become independent. Fledging occurs around 12 to 21 days post-hatching. As nestlings grow, they start to show signs of restlessness and begin to exercise their wings.
During this time, the parents continue to provide food, but they also encourage independence by allowing the chicks to leave the nest for brief periods. This process is critical for the finches to develop their flight skills, vital for evading predators and finding food.
Indicators of Readiness to Fledge:
- Wing Flapping: Increased wing flapping indicates readiness for flight.
- Vocalizations: Fledglings start to chirp and communicate more.
Anatomical Features of Finch Nestlings
Understanding the anatomical features of finch nestlings is crucial. Their physical structure plays a vital role in their growth and development, influencing their ability to survive in the wild. Each aspect is interrelated, supporting their nutrition, mobility, and overall health.
Physical Characteristics
Finch nestlings exhibit unique physical characteristics that are important for their adaptation. At birth, nestlings are altricial, meaning they are born helpless, blind, and without feathers. Their skin appears pink and wrinkled, which may seem unappealing, but this softness promotes insulation and warmth during the early days.
As they grow, feathers gradually emerge, starting with down feathers. These soft initial feathers provide insulation but do not allow for flight. The beak of a finch nestling is particularly noteworthy. It tends to be larger in proportion to its body, aiding in feeding, especially when it seeks food from its parents.
"The remarkable growth of finch nestlings transforms them significantly from a helpless state to vibrant fledglings."
It is essential also to consider their legs and feet. Nestlings have relatively short legs in the early stages. During growth, these limbs strengthen and develop to enable nestlings to cling securely as they transition into the fledging stage. The development of their feet’s gripping abilities is crucial for their survival.
Overall, the anatomical structure of finch nestlings lays a foundation for their gradual transition. Each physical characteristic is a step in their development, influencing overall survival in their natural environment.
Sensory Development
The sensory development of finch nestlings is vital for their interaction with the world around them. From the moment they hatch, their senses start to evolve rapidly. While their eyes are closed at birth, they begin to open within a few days. The eyesight improves dramatically, enabling them to recognize their parents visually. Vision is paramount for seeing food or spotting threats.
Hearing is another crucial sense. While it is not as developed at hatching, nestlings quickly start to respond to sounds in their environment. They can identify their parents’ calls, enhancing their feeding experience.
Taste and smell in finch nestlings are initially less pronounced. However, as they grow, these senses also become refined. The ability to taste helps them learn what foods are safe, guiding them as they transition from dependence on their parents for food.
The interaction between these sensory systems sets the groundwork for their social behaviors. As they develop, they start to interact more with each other. This interaction helps in honing their social skills, which are vital in establishing social structures within flocks later on.
The integration of sensory development is a complex process that facilitates a nestling's survival and integration into their environment, ultimately shaping their future as adult birds.
Parental Care of Finch Nestlings


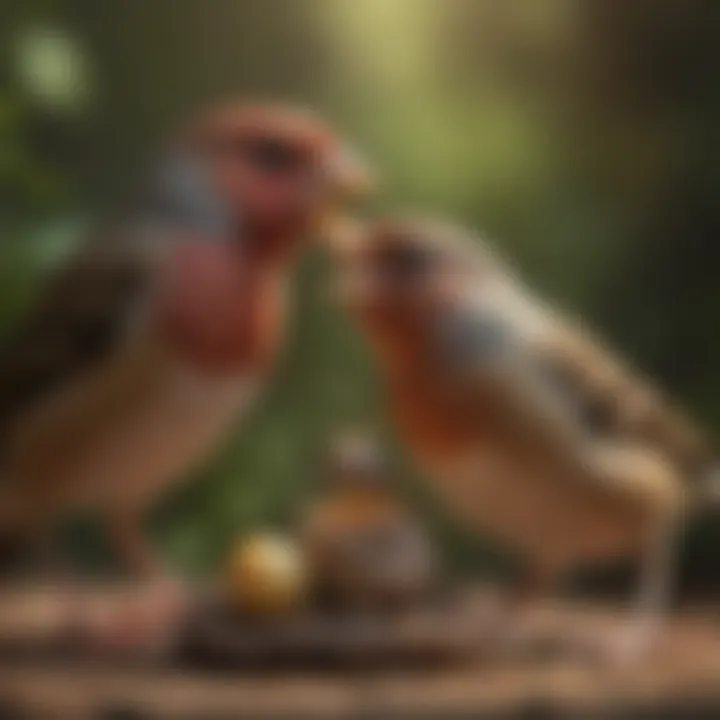
Parental care is crucial for the survival and development of finch nestlings. This process involves both female and male finches working together to ensure their offspring grow healthy. The importance of this care cannot be overstated. The first few weeks of a nestling's life are particularly vulnerable. During this time, parental investment directly impacts survival rates.
A significant aspect of parental care in finches is feeding. Nestlings rely on their parents for food, warmth, and protection from predators. The quality of care received during these formative days sets the stage for their future success. Understanding how both parents contribute to this process helps in appreciating their complex behaviors.
Role of the Female Finch
The female finch plays a primary role in raising nestlings. She is responsible for building the nest and incubating the eggs. Once the eggs hatch, her role shifts to intensive care for the young. The female often prioritizes feeding and brooding. She uses her body heat to keep the nestlings warm, especially during cooler temperatures. Her role is not merely limited to nurturing; the female also actively seeks food to supply the demanding young.
Moreover, female finches exhibit strong protective instincts. They can detect threats nearby and will defend the nest aggressively if needed. This protective behavior is essential as it helps safeguard the vulnerable nestlings from potential predators. The commitment shown by the female finch is crucial for fostering a safe environment for early growth.
Involvement of the Male Finch
The male finch complements the efforts of the female. Although his role is often less pronounced in nurturing, it remains vital. Male finches generally provide food and help protect the nesting site. This includes defending against intruders and potential threats, ensuring females can focus on their immediate caregiving tasks.
Beyond protection, male finches also participate in feeding. They will bring food back to the nest and sometimes even feed the female, allowing her to return to brooding. This teamwork helps the nestlings receive the nourishment necessary for rapid growth. The male's involvement signifies the importance of collaboration in raising young finches.
Feeding Techniques
Feeding techniques employed by finch parents are varied and adaptive. Both parents typically engage in a behavior known as "beak-to-beak" feeding. This occurs when adult finches regurgitate food directly into the mouths of their nestlings. This method is efficient, as it allows the young to receive a mix of nutrients quickly.
In the wild, finch diet consists of seeds, insects, and fruits. As such, parents forage for these diverse food sources. They selectively gather items rich in protein and fat for the growing nestlings, essential for their development. The parents are very attentive to the nutritional needs of their young, adjusting their diet based on availability and nestling demands.
Research indicates that the variation in diet can significantly influence the growth rates of finch nestlings. Richer diets contribute to improved health and better chances of fledging successfully.
Nutritional Needs of Finch Nestlings
The nutritional needs of finch nestlings are central to their growth and development. Proper nutrition directly influences their survival rates and overall health. Finch nestlings require a mix of proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals to thrive. Understanding these needs can aid in the successful care of these young birds, particularly for enthusiasts and breeders.
Dietary Requirements
Dietary requirements for finch nestlings can vary with species, but the general needs remain consistent. They primarily need a high-protein diet, especially during the early stages of development. Protein is essential for muscle development and tissue growth.
Some key dietary components include:
- Proteins: Integral for growth and repair.
- Fats: Provide energy and support healthy brain development.
- Vitamins: Essential for physiological functions and immunity.
- Minerals: Important for bone development and maintaining overall health.
Feeding them specialized formulas designed for orphaned birds can be beneficial. This ensures that they receive the necessary nutrients in an easily digestible form.
Food Sources in the Wild
In their natural habitat, finch nestlings depend on their parents to provide food. The predominant food sources include seeds, insects, and fruits. Each type of food contributes different nutrients necessary for the young birds’ growth. Some common food sources are:
- Seeds: Provide carbohydrates and fats.
- Insects: A rich protein source for growing nestlings.
- Fruits: Deliver vitamins and hydration.
It’s important to note that the availability of these food sources can be affected by environmental changes. A loss of habitat diminishes food supplies, posing threats to the nestlings’ survival. Conservation efforts must include measures to protect these natural food sources to maintain healthy populations of finches.
Behavioral Aspects of Finch Nestlings
The study of behavioral aspects in finch nestlings provides valuable insights into their survival and development. Understanding their behaviors allows pet owners and bird enthusiasts to better appreciate their needs. Furthermore, it helps conservationists develop targeted strategies for protecting these vulnerable birds. Each behavior signifies important underlying processes in their growth and adaptation to their environment.
Communication Signals
Communication is essential for nestlings in several ways. Young finches express needs through various signals, which can include vocalizations and body language. For instance, they often chirp or call out when hungry or in distress. These sounds serve as alerts to their parents regarding their physiological needs, increasing the chances of timely feeding and care from adult finches.
Nestlings also utilize physical gestures. Fluttering wings or specific movements can indicate excitement or readiness for interaction. Such behaviors are critical for forming a bond with parents, facilitating nurturing and safety.
Engaging in these communication signals enhances the social learning process. Young finches can learn social cues from their siblings and parents. This learning translates to more effective interactions within their environment as they mature.
Social Interactions
Social interactions among finch nestlings play a crucial role in their behavioral development. Nestlings often engage with siblings in a cooperative manner. Sharing space in the nest means they must learn to coexist and communicate effectively. This dynamic not only fosters social bonds but also allows them to develop essential survival skills.
As nestlings grow, they become increasingly active. They start to explore their surroundings, which encourages interactions with each other. These play behaviors are a form of practice for the finches' future adult social behaviors. Observations show that nestlings that engage in active play demonstrate heightened adaptability to their environment once fledged.
Parental presence also influences social interactions significantly. For instance, nestlings often mimic adult behaviors, learning how to forage and communicate. This imitation is crucial for their upcoming independence.
The developmental stage of nestlings is rich in opportunities for social learning, laying a foundation for their future interactions in the wild.
Habitat and Nesting Preferences
Understanding the habitat and nesting preferences of finch nestlings is crucial for anyone interested in their development, care, and conservation. Habitat plays a vital role in the survival and wellbeing of finch species. Proper nesting conditions can influence the success of brooding and the health of nestlings. It is essential to recognize the specifics of where finch nestlings thrive to create environments that facilitate their growth and reduce their susceptibility to predators and environmental threats.
Ideal Nesting Conditions
Finch nestlings prefer sheltered, secure environments for nesting. These conditions reduce the risk of predation and adverse weather. The following factors contribute to ideal nesting conditions:
- Location: Nesting sites should be away from heavy foot traffic and disturbances from humans and animals. Dense foliage or shrubs often provide the best cover.
- Material Availability: Finch nests are typically constructed using grass, feathers, and bits of bark. Having abundant supplies of these materials nearby encourages nesting.
- Climate: Moderate climates are preferred by many finch species. Extreme temperatures can impact egg incubation and the health of nestlings.
An understanding of these factors helps in recognizing suitable areas for nesting, thereby contributing to the protection and fostering of local finch populations.
Common Nesting Sites
Finch nestlings are highly adaptable and find nesting locations in a variety of settings. Common sites include:
- Thickets and Dense Brush: Many finches prefer dense areas. These locations offer safety and protection from predators.
- Trees: Certain finch species, such as House Finches, often build nests in trees, particularly in the forks of branches or on horizontal limbs.
- Human Structures: Interestingly, some finches have adapted to nest in urban environments. This includes eaves of buildings, hanging planters, and even inside sheds.


The choice of nesting site can significantly affect their development, making it important to monitor these areas for conservation efforts. Understanding these nesting preferences can aid in creating supportive environments for finch populations.
Threats to Finch Nestlings
The survival of finch nestlings hinges significantly on various threats present in their environments. Understanding these threats is crucial for establishing effective conservation strategies. Predation and environmental changes are two primary factors impacting the life and development of finch nestlings. Each poses unique challenges that require careful consideration by bird enthusiasts, conservationists, and even casual observers.
Predation Risks
Predation represents one of the most severe threats to finch nestlings. Many natural predators, such as cats, hawks, and snakes, actively hunt young birds in their nests. This danger is compounded for species that nest on or near the ground, making them particularly vulnerable.
The impact of predation is not just a matter of individual loss; it can have cascading effects on local finch populations. For example, if a significant number of nestlings are lost to predators, the breeding success of adult finches declines, leading to potential population decreases over time. Identifying suitable nesting locations can help minimize these risks.
To mitigate predation, creating awareness is important among the community, emphasizing responsible pet ownership. Encouraging cat owners to keep their cats indoors can drastically reduce predation risks for finch nestlings.
Environmental Changes
Environmental changes pose another major threat to finch nestlings. Climate change, habitat destruction, and urbanization lead to alterations in their natural habitats. For instance, changes in temperature and rainfall can affect food availability, nesting sites, and even migration patterns.
As forests are cleared for agricultural or urban developments, the safe nesting environments for finches diminish. Nestlings rely on specific habitats that provide suitable food sources and cover from predators. The degradation of these environments can lead to decreased nesting success and survival rates.
Furthermore, extreme weather events, such as storms and droughts, can disrupt the breeding season, making it difficult for nestlings to thrive. Conservation efforts need to focus not only on protecting existing habitats but also on restoring degraded areas to support the survival of finch nestlings.
In summary, understanding the threats of predation and environmental changes is vital for ensuring the survival and development of finch nestlings. By addressing these issues, we contribute positively to the broader ecosystem and the health of finch populations.
Conservation Efforts for Finch Nestlings
Conservation efforts play a vital role in ensuring the survival and well-being of finch nestlings. These initiatives are essential to address the challenges that these birds face due to habitat loss, predation, and environmental changes. Protecting finch nestlings guarantees the continuation of not only their species but also the ecological balance within their habitats. When communities engage in conservation, they create a supportive environment for nestlings to thrive.
Community Involvement
Community involvement is crucial for the conservation of finch nestlings. Local initiatives can take various forms, such as creating awareness campaigns, organizing habitat restoration projects, and supporting wildlife-friendly practices.
- Education Programs: Schools and organizations can promote education with workshops that teach children and adults about the importance of finch nestlings and how to protect them.
- Citizen Science: Engaging community members in monitoring local bird populations can provide valuable data for scientists while fostering a sense of stewardship among participants.
- Habitat Restoration: Volunteer groups can work together to restore natural environments. This may include planting native vegetation or removing invasive species that threaten finch habitats.
- Feeding Stations: Establishing safe feeding stations can help provide essential food sources for finch nestlings, particularly during harsh weather or food shortages.
The impact of community involvement can significantly enhance the chances of survival for finch nestlings, as both awareness and action lead to better protection measures.
Legislative Actions
Legislative actions are another important aspect of conserving finch nestlings. Policies and regulations can directly protect habitats and enforce measures that mitigate threats. Several areas of focus exist:
- Protected Areas: Creating and maintaining protected areas ensures that finch nestlings have safe environments where they can nest and grow without significant human interference.
- Regulation of Habitat Destruction: Enforcing laws that limit deforestation, urban expansion, and pollution can greatly benefit finch populations.
- Species Protection: Lobbying for the protection of specific finch species under national and international legislation can help in elevating the status of these birds and securing funding for conservation programs.
- Funding for Research: Legislative backing can also secure funds for research. This research is critical to understanding the biology, behaviors, and requirements of finch nestlings, which can guide further effective conservation strategies.
Governments and non-profit organizations must collaborate to implement these legislative measures effectively.
"The survival of finch nestlings depends not only on individual efforts but also requires a collective commitment to create sustainable environments and enforce protective laws."
Caring for Finch Nestlings: Guidelines for Enthusiasts
Caring for finch nestlings is an essential aspect of ensuring the survival and healthy development of these young birds. For those who may encounter a nestling, whether through foundlings or breeding initiatives, understanding best practices can greatly enhance their chances of success. This section will clarify the critical considerations when caring for these delicate creatures, emphasizing the momentous benefits that arise from informed intervention.
First, it is vital to recognize that this undertaking demands both patience and knowledge. Finch nestlings, although resilient, require specific care reflective of their physiological and developmental stages. By knowing when to step in, and understanding best practices for rehabilitation, enthusiasts can forge a significant impact on a nestling's quality of life. The following will elaborate on how to effectively provide care while also allowing for growth and natural behaviors to flourish.
When to Intervene
Several key indicators suggest that intervention may be necessary when it comes to finch nestlings. One fundamental aspect is the observation of the nestling's condition and surroundings.
- Abandonment: If a nestling is found away from its nest, it may signal abandonment. Young birds that are newly fledged might appear lost but can often be left alone. However, if it shows signs of distress or is injured, action should be taken.
- Injury: Any visible injuries, such as bleeding or broken feathers, deem immediate attention. Bringing the injured bird to a trained wildlife rehabilitator is advisable.
- Not Feeding: If a nestling is not feeding for extended periods, this can indicate a significant issue.
- Extreme Weather: Harsh weather conditions may necessitate rescue if the nest is compromised. Protecting a nest against heavy rain or predators is imperative.
Make sure to verify your involvement is necessary. Sometimes, natural parental care is sufficient.
Best Practices for Rehabilitation
When preparing for rehabilitation, enthusiasts should adhere to sound practices aimed at minimizing stress for the nestling. The following points are crucial to ensure a successful rehabilitation process:
- Create a Safe Space: Establish a quiet and secure area for the nestling. Avoid loud noises and keep other pets away to reduce stress levels.
- Nutrition: It is essential to provide the correct type of food. For finch nestlings, a mixture of soft, high-protein foods such as blended bird feed, soft fruits, and insects is beneficial. Always ensure that the food is age-appropriate.
- Hydration: Providing water is also crucial but must be done carefully. A shallow dish is ideal for older nestlings. For younger ones, hydration is often achieved through food.
- Monitoring: Regularly check on the nestling’s progress. Look out for signs of improvement, like increased energy and weight gain. Adjust care practices based on its needs as it develops.
It is essential to remember that some interventions require specialized care. Connecting with wildlife rehabilitation centers can provide access to more comprehensive support.
- Reintegration: If you decide to release the nestling back into the wild, do so with caution. Ensure the area is safe and that it can fend for itself before letting it go. A gradual introduction to the wild can sometimes be useful.
Overall, caring for finch nestlings is a rewarding yet challenging endeavor. By understanding when to act and applying best practices for their rehabilitation, enthusiasts can significantly contribute to the health and survival of these birds. This not only aids individual nestlings but also supports the broader conservation efforts dedicated to these fascinating species.
Epilogue
The conclusion of this article plays a vital role in synthesizing the information discussed about finch nestlings. It is crucial to understand that finch nestlings are vulnerable yet resilient creatures, needing informed care and concerted conservation efforts to thrive. The section encapsulates the significance of grasping their developmental needs, the essential role of parental care, and the pressing threats they face in their environment.
By highlighting these elements, the conclusion emphasizes the benefits of awareness and understanding among pet owners, animal lovers, and families with children. Through education, stakeholders can better support the healthy development and conservation of finch nestlings.
Moreover, the conclusion reinforces the idea that by taking proactive measures, we can ameliorate the numerous environmental challenges that these birds encounter. This understanding promotes responsible actions such as habitat preservation and implementation of best practices in care, ensuring a lasting positive impact on the finch population.
Summary of Key Points
- Biological Development: Finch nestlings undergo distinct stages of growth that necessitate specific environmental supports.
- Parental Care: Both female and male finches contribute significantly to nurturing their young, ensuring proper conditioning through effective feeding techniques.
- Nutritional Needs: Proper diet is essential for nestlings, consisting of protein-rich foods that aid in their rapid growth phases.
- Environmental Threats: Finch nestlings face risks from predation as well as habitat loss due to urbanization and climate change.
- Conservation Efforts: Community and legislative efforts are crucial for protecting the habitats that sustain finch populations.
This summary underscores the complexity of finch nestlings’ lives and their interdependence on both natural and human systems, underscoring the need for ongoing education and intervention.
Future Directions in Finch Conservation
Looking ahead, the future of finch conservation requires a multi-faceted approach. Key directions include:
- Research Initiatives: Continued study on nesting behaviors and developmental patterns can improve understanding and enhance conservation strategies.
- Community Engagement: Encouraging local involvement in conservation projects can lead to better habitat management and increased awareness of the issues finches face.
- Legislative Support: Advocacy for protective laws and policies is essential to secure safe environments for finch populations.
- Education Programs: Creating educational resources aimed at schools and community organizations can foster appreciation and care for these birds.
Integration of these factors will create a sustainable pathway for the conservation of finch nestlings. By focusing on science, community, and education, we can work toward a future where these beautiful birds continue to thrive in their natural habitats.







